The new Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA) represent a major improvement over previous guidelines. The storm of criticism registered by some “experts” and quoted by the media is NOT based on valid evidence. There has been excessive and irrational criticism over inverting the food pyramid, with animal sources of protein on the top. Until now recommendations for daily protein intake have been based upon estimates to avoid protein deficiency rather than optimization. The recommendations for 1.2-1.6 grams per kilogram bodyweight per day (up from 0.8 g/kg/day) is supported by data on muscle building, muscle maintenance and bone health (when combined with resistance exercise), especially for elderly individuals.
Unfortunately, the 10% restriction on saturated fat remains, but the guidelines appropriately state that there is a lack of evidence to keep that restriction at 10% of caloric intake. The controversy over saturated fat remains despite meta-analyses of randomized controlled clinical trials that conclude that restriction of saturated fat has not been found to improve cardiovascular, metabolic, or cancer outcomes.
I doubt that those critical of the new DGA have read the 416-page appendices that document scientific references and explanations for each of the dietary recommendations. That’s right, 416 pages of narrative and scientific references are in the appendices of the DGA.
If you go here, you can download 4 documents including the Scientific Foundation Appendices (416 pages), the Scientific Foundation for DGA (90 pages), The Daily Servings Guide (3 pages) and the DGA (10 pages)
Here is an excerpt that is very useful.
How can you identify highly processed foods? Highly processed foods tend to have: 1. Refined grains and/or added sugars 2. Refined fats and oils 3. Long, complicated ingredient lists including chemical additives (e.g., artificial sweeteners, flavor enhancers, artificial colors, and emulsifiers). Examples are provided in Figures 4.3 and 5.8.
And a good explanation for why refined grains (any food made with flour) causes rapid and high blood sugar responses.
Refined Grains and Starches are Sugar • Refined grains are highly purified sources of starch. • Starches are long chains of glucose—a form of sugar. • During chewing and digestion, enzymes rapidly break down starch into glucose, raising blood sugar much like table sugar does. • Refined grain foods—white bread, crackers, breakfast cereals, chips, pastries, and pasta—can therefore act metabolically like sugar, delivering fast-absorbing carbohydrates with few nutrients or fiber to slow absorption. Take-home message: Refined grains are sugar in disguise. Choose whole grains, beans, or vegetables instead.
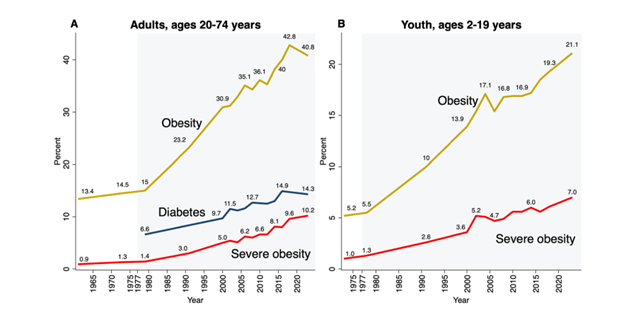
The following two graphics demonstrate the results of previous dietary guidelines that demonized healthy fats and animal sources of protein. The first shows the rise in obesity and diabetes but does not address the insulin resistance that evolves over decades before crossing the arbitrary threshold of diabetes, wreaking metabolic havoc long before diabetes occurs. The second graphic reveals how Americans consume 60% or more caloric intake in the form of refined carbohydrates (equivalent to sugar)
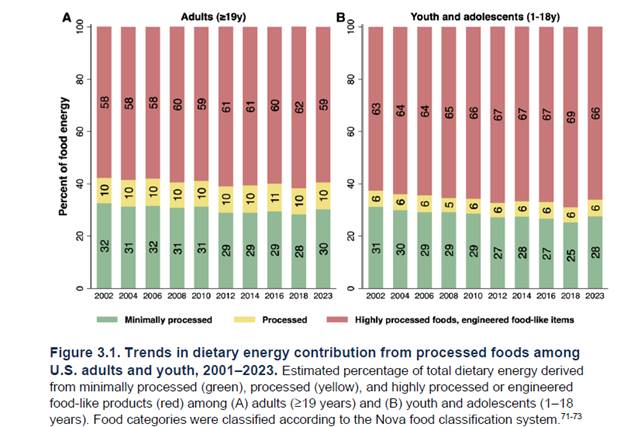
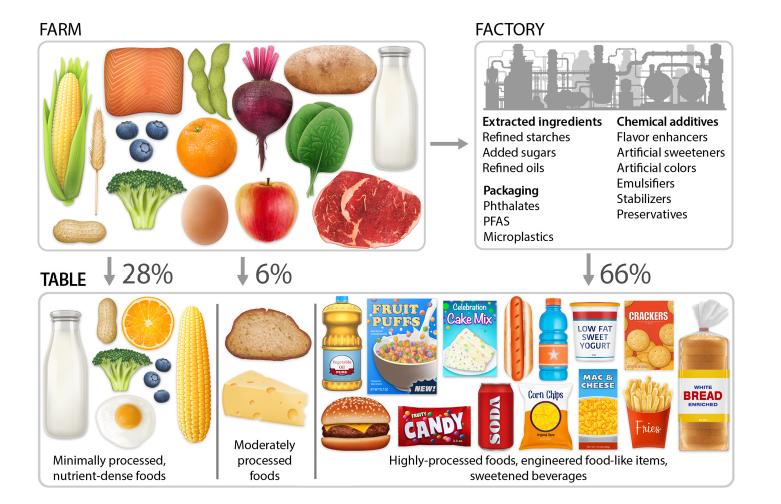
The following graphic displays the difference between minimally processed, moderately processed and highly processed foods according to the NOVA classification system (a system I will discuss and criticize in future posts). For now, suffice it to say that a simpler and more practical definition of “processed food” would include any food with one or more of the following: added sugar, artificial sweeteners, refined starch especially flour made from grains, refined “vegetable” oils, emulsifiers, artificial coloring, preservatives, and other additives found to disrupt the microbiome, intestinal barrier function or cause cancer. This graphic importantly covers the issue of food packaging which can contribute to the consumption of micro plastics, phthalates and PFAs
I have consistently advocated for a diet that consists of free-range meat, poultry, eggs, seafood (low mercury varieties), organic vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, an ancestral or paleo diet. The new DGA go a long way to produce evidence-based recommendations to help Americans eat healthy food. I continue to advocate for getting fiber from vegetables and fruits, eliminating grains, for reasons previously discussed but if you want to eat grains and are not gluten sensitive or suffer from celiac disease, consume the grains as a whole food, not in a food made from flour. “Whole grain bread” is not a whole grain food, nor is “whole grain” pasta. Once flour is made from grains the cellular components are destroyed producing a product with a glycemic index akin to sugar with the resultant metabolic disturbance which over the long run leads to insulin resistance, obesity and chronic disease.
If you want to consume dairy it makes much more sense to consume full fat fermented dairy foods instead of the low-fat dairy products advocated by prior DGA. The new DGA go into great detail to describe the nutrient deficiencies associated with vegan and vegetarian diets unless specific supplements are consumed. Specific recommendations for pregnant and breast-feeding mothers cover most important points as do age specific recommendations for infants and children. The importance of choline could have received a little more attention (best sources include eggs and liver). The importance of marine omega-3 fats (EPA, DHA, DPA) received adequate attention.
Overall, I consider the 2026 DGA a major improvement compared to previous iterations which ignored a large body of nutritional science.
The following references support my position on SFA and properly raised and prepared animal protein.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32562735/
Astrup A, Magkos F, Bier DM, Brenna JT, de Oliveira Otto MC, Hill JO, King JC, Mente A, Ordovas JM, Volek JS, Yusuf S, Krauss RM. Saturated Fats and Health: A Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Aug 18;76(7):844-857. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.05.077. Epub 2020 Jun 17. PMID: 32562735.
Reimara Valk, James Hammill, Jonas Grip, Saturated fat: villain and bogeyman in the development of cardiovascular disease?, European Journal of Preventive Cardiology, Volume 29, Issue 18, December 2022, Pages 2312–2321, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjpc/zwac194
Associations of fats and carbohydrate intake with cardiovascular disease and mortality in 18 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study Dehghan, MahshidDiaz, R et al. The Lancet, Volume 390, Issue 10107, 2050 – 2062
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36216940/
Lescinsky H, Afshin A, Ashbaugh C, Bisignano C, Brauer M, Ferrara G, Hay SI, He J, Iannucci V, Marczak LB, McLaughlin SA, Mullany EC, Parent MC, Serfes AL, Sorensen RJD, Aravkin AY, Zheng P, Murray CJL. Health effects associated with consumption of unprocessed red meat: a Burden of Proof study. Nat Med. 2022 Oct;28(10):2075-2082. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01968-z. Epub 2022 Oct 10. PMID: 36216940; PMCID: PMC9556326.
Red and processed meat consumption and risk of incident coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis Renata Micha1, Sarah K Wallace, Dariush Mozaffarian, Circulation CIRCULATIONAHA.109.924977. Epub 2010 May 17. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20479151/
Unprocessed Red Meat and Processed Meat Consumption: Dietary Guideline Recommendations from the Nutritional Recommendations (NutriRECS) Consortium Bradley C. Johnston, PhD, Dena Zeraatkar, Msc, et. al. Ann Intern Med 2019: 1:756-764 doi: 10.7326/M19-1621
Reduction of Red and Processed Meat Intake and Cancer Mortality and Incidence A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies Mi Ah Han, MD, PhD; Dena Zeraatkar, MSc; et. al., Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:711-720. doi:10.7326/M19-0699
Patterns of Red and Processed Meat Consumption and Risk for Cardiometabolic and Cancer Outcomes A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies Robin W.M. Vernooij, PhD*; Dena Zeraatkar, MSc Ann Intern Med.2019;171:732-741. doi:10.7326/M19-1583
Red and Processed Meat Consumption and Risk for All-Cause Mortality and Cardiometabolic OutcomesA Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies Dena Zeraatkar, MSc, Mi Ah Han MD, PhD, et. al, Annals of Internal Medicine 1 October 2019: 171-710 doi: 10.7326/M19-0655
Effect of Lower Versus Higher Red Meat Intake on Cardiometabolic and Cancer Outcomes
A Systematic Review of Randomized Trials Dena Zeraatkar, MSc, Bradley C Johnston, PhD, et. al. Ann Intern Med. 2019;171:721-731. doi:10.7326/M19-https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-0622
E, Lavie CJ, Hill JO. The Failure to Measure Dietary Intake Engendered a Fictional Discourse on Diet-Disease Relations. Front Nutr. 2018 Nov 13;5:105. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00105. PMID: 30483510 Archer; PMCID: PMC6243202.
Archer E, Hand GA, Blair SN (2013) Validity of U.S. Nutritional Surveillance: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Caloric Energy Intake Data, 1971–2010. PLoS ONE 8(10): e76632. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076632
O’Connor, Lauren E., et al. “Effects of total red meat intake on glycemic control and inflammatory biomarkers: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.” Advances in Nutrition 12.1 (2021): 115-127.
Kiani AK, Dhuli K, Donato K, Aquilanti B, Velluti V, Matera G, Iaconelli A, Connelly ST, Bellinato F, Gisondi P, Bertelli M. Main nutritional deficiencies. J Prev Med Hyg 2022;63(suppl.3):E93-E101.https://doi.org/10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.2S3.2752
Bailey RL, West KP Jr, Black RE. The epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;66 Suppl 2:22-33. doi: 10.1159/000371618. Epub 2015 Jun 2. PMID: 26045325.
Global, regional and national burdens of common micronutrient deficiencies from 1990 to 2019: A secondary trend analysis based on the Global Burden of Disease 2019 study. Zu Han et. al., eClinicalMedicine, February 11, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101299
Sean R. Lynch, Why Nutritional Iron Deficiency Persists as a Worldwide Problem, The Journal of Nutrition, Volume 141, Issue 4, April 2011, Pages 763S–768S, https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.110.130609
Meat supplementation improves growth, cognitive, and behavioral outcomes in Kenyan children , J Nutr. 2007 Apr;137(4):1119-23.
Animal source foods have a positive impact on the primary school test scores of Kenyan schoolchildren in a cluster-randomised, controlled feeding intervention trial – PubMed (nih.gov), Hulett JL, Weiss RE, Bwibo NO, Galal OM, Drorbaugh N, Neumann CG.Br J Nutr. 2014 Mar 14;111(5):875-86. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513003310. Epub 2013 Oct 30.PMID: 24168874 Clinical Trial.
Meat supplementation increases arm muscle area in Kenyan schoolchildren – PubMed (nih.gov), Br J Nutr. 2013 Apr 14;109(7):1230-40. doi: 10.1017/S0007114512003121. Epub 2012 Aug 2.PMID: 22856533 Clinical Trial.
Neumann CG, Bwibo NO, Jiang L, Weiss RE.Public Health Nutr. 2013 Sep;16(9):1593-604. doi: 10.1017/S1368980013000876. Epub 2013 Mar 28.PMID: 23537728
Allen LH, Dror DK.Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2011;67:113-30. doi: 10.1159/000325579. Epub 2011 Feb 16.PMID: 21335994
https://www.bmj.com/content/351/bmj.h4962
The scientific report guiding the US dietary guidelines: is it scientific?
BMJ 2015; 351 doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.h4962 (Published 23 September 2015)
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9794145/
Teicholz N. A short history of saturated fat: the making and unmaking of a scientific consensus. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2023 Feb 1;30(1):65-71. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000791. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Erratum in: Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2025 Aug 1;32(4):166. doi: 10.1097/01.med.0001118356.22843.75. PMID: 36477384; PMCID: PMC9794145.
THIS WEBSITE PROVIDES INFORMATION FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. CONSULT YOUR HEALTH CARE PROVIDER FOR MEDICAL ADVICE.
Eat clean, drink filtered water, love, laugh, exercise outdoors in a greenspace, get some morning sunlight, block the blue light before bed, engage in meaningful work, find a sense of purpose, spend time with those you love, AND sleep well tonight.
Doctor Bob