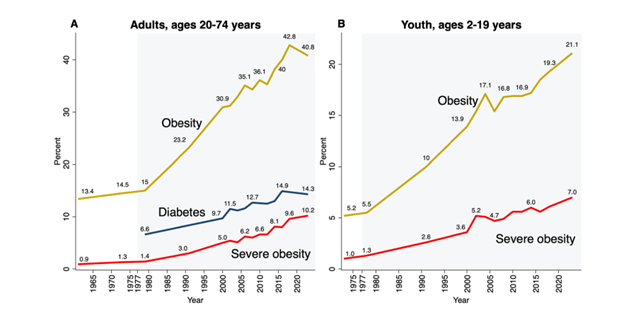
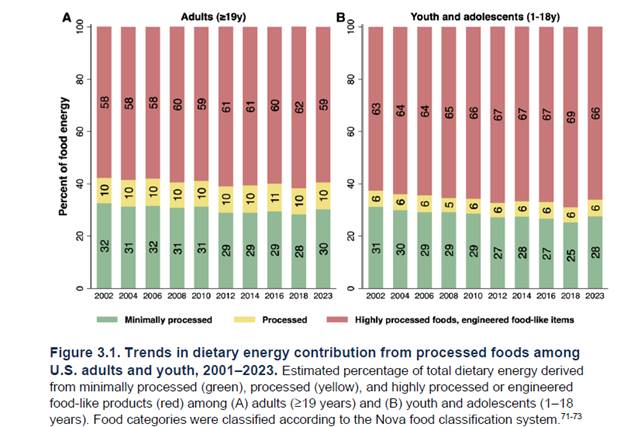
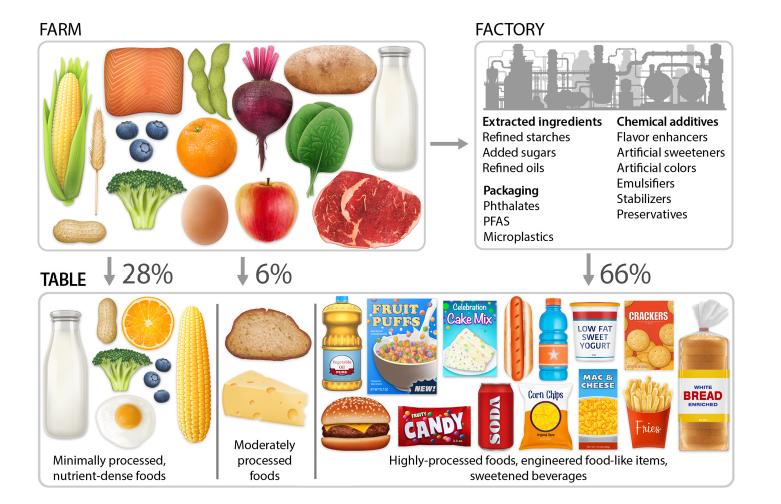
Insulin is much more than a blood sugar hormone. Produced by the pancreas primarily in response to carbohydrate and sugar consumption, insulin is a master anabolic signal that dictates how every cell in your body grows, uses energy, and repairs itself. When insulin levels are healthy, it keeps the body in a state of “build and store.” When insulin resistance (IR) develops, the body loses its ability to hear this signal, leading to systemic breakdown. Instead of “build and store” the body deteriorates, causing loss of muscle mass, strength, energy production, memory and cognitive function, bone strength, brain cells and connections, ability of blood vessels to relax, ability for the heart to pump blood, ability to achieve restorative sleep, ability of the liver and kidneys to clear toxins from the body, even the ability to reproduce resulting in infertility and erectile dysfunction. Visceral fat stores increase to destructive levels resulting in obesity and obesity-related complications including chronic inflammation which further drives IR to higher levels.
IR is a root cause of cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke, hypertension, heart failure), many kinds of cancer (directly linked to breast, prostate and colon cancer), kidney failure, heart failure, dementia, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and much more. IR is causally linked or a contributor to, every chronic non-communicable disease of modern civilization.
WHAT IS INSULIN RESISTANCE?
Insulin resistance is the inability of cells and organs to respond normally to insulin signaling. Every cell of every organ has insulin receptors that initiate action by the cell and organ.
WHAT CAUSES INSULIN RESISTANCE?
There are many causes of IR. Stress hormones (cortisol, adrenaline), inflammation, and high insulin levels themselves (response to dietary sugar and refined carbohydrates), each alone and in combination, cause immediate (within minutes to hours) insulin resistance. When these conditions persist over time insulin resistance becomes a chronic state. As fat cells grow in size, they reach a point where there is inadequate blood flow to the cells themselves and macrophages (immune cells that reside between the fat cells, most prominently in visceral fat) produce inflammatory chemicals called cytokines. Cytokines flow through the blood stream and effect every organ and every cell in the body creating a state of chronic inflammation which further worsens IR, creating a vicious cycle. As IR continues the pancreas produces increasingly higher amounts of insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels but eventually IR becomes so great that blood sugar levels move into the “pre-diabetes” and eventually the diabetes range. IR builds for years to decades before blood sugar regulation fails. By the time blood sugar levels are “abnormal” insulin resistance has done great damage throughout the body.
Most doctors tragically do not order fasting insulin levels as routine blood tests. Fasting insulin levels rise long before fasting blood sugars and hemoglobin A1c start to rise. Meanwhile the damage progresses under the radar of routine testing.
1. Metabolic Engines: Muscle and Liver
Muscle
- Normal Action: Insulin acts as a key that opens “doors” (GLUT4 receptors) to let glucose in for fuel. it also stimulates protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is essential to maintaining and increasing muscle mass and strength.
- Insulin Resistance Effect: The “doors” stay locked. Glucose stays in the blood, and the muscle becomes “starched,” leading to sarcopenia (muscle wasting) and fatigue. The muscle can no longer utilize dietary protein to maintain or increase muscle mass.
Liver
- Normal Action: Tells the liver to stop producing glucose and start storing it as glycogen or converting excess into fat.
- Insulin Resistance Effect: The liver ignores the “stop” signal and keeps pumping out glucose while simultaneously ramping up fat production. This results in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).
2. Fat Cells (Adipose Tissue)
Visceral (Deep Fat) vs. Subcutaneous (Under Skin)
- Normal Action: Insulin promotes fat storage and inhibits the breakdown of stored fat (lipolysis).
- Insulin Resistance Effect: Fat cells—especially visceral ones—become “leaky.” They spill free fatty acids into the bloodstream and release inflammatory cytokines. This causes weight gain that is biologically difficult to lose because high insulin levels keep the “fat-burning” switch permanently off.
3. The Vital Organs: Heart, Kidneys, and Arteries
Heart and Arteries
- Normal Action: Insulin stimulates the release of nitric oxide, which helps arteries relax and dilate.
- Insulin Resistance Effect: Nitric oxide production drops, causing arteries to stiffen (hypertension). High insulin also damages the endothelial lining, leading to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). This is the primary driver of heart failure, heart attacks and strokes.
Kidneys
- Normal Action: Helps regulate sodium reabsorption.
- Insulin Resistance Effect: The kidneys hold onto too much salt, increasing blood pressure. Over time, high blood sugar and inflammation damage the filtering units, leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD).
4. The Brain, Memory, and Sleep
Brain and Memory
- Normal Action: Insulin crosses the blood-brain barrier to regulate appetite and support synaptic plasticity (the basis of learning).
- Insulin Resistance Effect: Often called “Type 3 Diabetes,” brain IR starves neurons of energy and allows amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles to build up. Worse, the brain is unable to utilize glucose to meet energy demands it starts to malfunction. This is a direct pathway to Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. As the small arteries in the brain become atherosclerotic and unable to deliver adequate oxygen and nourishment to brain cells small areas of the brain become permanently damaged eventually leading to vascular dementia.
Sleep
- Insulin Resistance Effect: IR is heavily linked to Obstructive Sleep Apnea. (OSA) High insulin affects the central respiratory drive and increases fat deposits around the neck (a major contributor to obstructive sleep apnea), disrupting sleep cycles and creating periods of inadequate oxygen flow to the brain resulting in the acute stress response and awakening with each apneic event. Even without OSA, high insulin levels impair the production of melatonin which is essential to normal-restorative sleep. Throughout the day the brain accumulates metabolic toxins that must be cleared through the glymphatic system at night during sleep. As sleep is impaired this clearance system is disrupted, contributing to structural damage and functional loss. Sleep disruption and apneic episodes are stressful events, increasing stress hormones which then worsen IR, creating another vicious cycle. One night of sleep disruption causes acute IR. Chronic sleep disruption contributes to chronic IR.
5. Immunity and Structural Health
Immune System
- Action: High insulin/glucose impairs white blood cell function.
- Effect: Chronic inflammation (high CRP levels) and a weakened defense against infections. This is why diabetics often have poor wound healing. As normal immune regulation is impaired the immune system both over-reacts and under-reacts. Under-reaction increases risk of infection. Over-reaction produces cytokine storms seen with Covid-19 and other infections. Chronic inflammation worsens IR creating another vicious cycle. Chronic inflammation contributes to most chronic diseases.
Bone and Joints
- Action: Insulin is bone-building.
- Effect: IR leads to poor bone quality (despite high density) and osteoarthritis due to systemic inflammation and the “glycosylation” (sugar-coating) of joint cartilage, making it brittle.
6. The Pancreas: Beta and Alpha Cells
- Normal Action: Beta cells produce insulin; Alpha cells produce glucagon (which raises sugar). They balance each other.
- Insulin Resistance Effect:
- Beta Cells: Work overtime to produce massive amounts of insulin to compensate, eventually “burning out” and dying. This can produce per4manent irreversible damage to the pancreas.
- Alpha Cells: Become resistant to insulin’s “stop” signal and keep secreting glucagon, further raising blood sugar levels which in turn cause higher insulin secretion, both of which worsen IR, creating another vicious cycle.
7. Reproductive Effects: Infertility
- In Women: High insulin stimulates the ovaries to produce excess testosterone, which is the primary driver of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and infertility.
- In Men: IR is a leading cause of low testosterone and erectile dysfunction (due to the arterial damage mentioned above).
Summary of Systemic Effects
| Condition | Primary Mechanism of Insulin Resistance |
| Atherosclerosis | Endothelial dysfunction, high triglycerides, low HDL, increased TG/HDL ratio, increased small dense LDL and remnant particles, increased endothelial permeability. |
| Dementia | Neuronal glucose starvation and plaque buildup, brain small vessel disease, disruption of blood brain barrier. |
| Chronic Inflammation | Release of cytokines from visceral fat. |
| Heart Failure | Stiffening of the heart muscle and high blood pressure. |
| Diabetes | Pancreatic beta cell and alpha cell damage |
Insulin’s Role vs. Insulin Resistance (IR)
| Organ/System | Normal Insulin Action | Effects of Insulin Resistance |
| Liver | Stops glucose production; stores glucose as glycogen. | The liver ignores the “stop” signal, pumping out sugar even when you haven’t eaten (fatty liver).Fatty liver disease is the greatest cause of liver failure in the US. |
| Muscle | Primary site for glucose uptake; promotes protein synthesis. | Muscles can’t take in fuel efficiently, leading to fatigue and muscle wasting (sarcopenia). Muscle cells cannot use amino acids from dietary protein to maintain or build muscle. Elderly lose muscle and strength, resulting in falls, fractures and head trauma. Loss of muscle (the major sink for blood sugar after a meal) further increases duration and degree of blood sugar and insulin rise after a meal, which in turn increases IR. (vicious cycle) |
| Fat (Adipose) | Stores fat; inhibits the breakdown of stored fat. | Fat cells leak fatty acids into the blood, leading to high triglycerides and visceral fat gain. Macrophages (immune cells) produce inflammatory cytokines which circulate through the body contributing to chronic inflammation which worsens IR, another vicious cycle. |
| Brain | Regulates appetite, memory, and cognitive function. | Linked to “Type 3 Diabetes”; impaired memory and increased risk of neurodegeneration. Brain loses ability to meet energy demands and clear toxins. Insulin resistance in the brain explains memory loss, cognitive impairment, loss of neurons and synapses, loss of neuroplasticity. BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor) production is decreased by IR. |
| Arteries | Stimulates nitric oxide for vasodilation (keeps vessels flexible). | Reduced nitric oxide causes vessels to stiffen, raising blood pressure and plaque buildup. This is called endothelial dysfunction, the precursor to heart attack, stroke, peripheral vascular disease and a root cause for neuropathy and amputations. |
| Heart | Regulates fuel use (switching between glucose and fats). | The heart becomes “metabolically inflexible,” increasing the risk of heart failure. |
| Kidney | Manages sodium reabsorption and filtration. | High insulin causes the kidneys to hold onto salt, driving up blood pressure and damaging filters. Oxidative stress leads to kidney failure. |
| Immune System | Modulates inflammation and helps T-cell function. | Creates a state of “chronic low-grade inflammation” and weakens the response to infections. |
| Bone | Stimulates bone-forming cells (osteoblasts). | Bone quality decreases; despite higher bone density in some cases, the bones are more brittle. |
| Joints | Maintains cartilage and reduces systemic inflammation. | High insulin promotes pro-inflammatory cytokines, accelerating osteoarthritis and gout. |
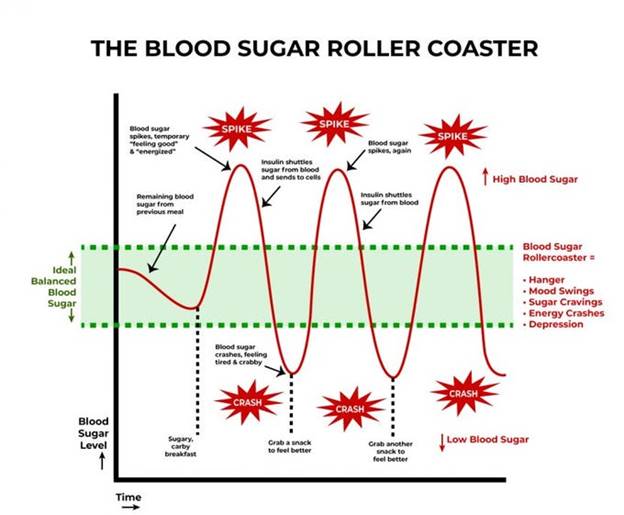
A meal with sugar and refined carbohydrates causes excessive swings in blood sugar and insulin levels, creating insulin resistance and downstream damage. Alcohol consumption contributes to this process. Fat consumption does not cause a rise in blood sugar or insulin levels. Protein consumption produces a minimal rise in insulin levels in the absence of IR.
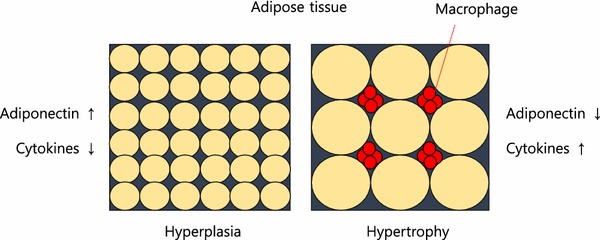
Fat storage can occur through hyperplasia (increase in number of fat cells) or hypertrophy (increase in size). Some ethnic groups are more prone to hypertrophy (south and east Asian). Hypertrophy in visceral fat (fat around the internal organs as opposed to fat under the skin) results in macrophage production of inflammatory cytokines. Eventually, the fat cells themselves can literally burst from too much volume.
In my next post, I will discuss what we can do to prevent and reverse IR.
REFERENCES
Chadt A, Al-Hasani H. Glucose transporters in adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle in metabolic health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020 Sep;472(9):1273-1298. doi: 10.1007/s00424-020-02417-x. Epub 2020 Jun 26. PMID: 32591906; PMCID: PMC7462924.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7462924/
Fujita S, Rasmussen BB, Cadenas JG, Grady JJ, Volpi E. Effect of insulin on human skeletal muscle protein synthesis is modulated by insulin-induced changes in muscle blood flow and amino acid availability. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;291(4):E745-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00271.2005. Epub 2006 May 16. PMID: 16705054; PMCID: PMC2804964.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2804964
Vargas E, Joy NV, Carrillo Sepulveda MA. Biochemistry, Insulin Metabolic Effects. [Updated 2022 Sep 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525983/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525983/
Bugianesi E, Moscatiello S, Ciaravella MF, Marchesini G. Insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Pharm Des. 2010 Jun;16(17):1941-51. doi: 10.2174/138161210791208875. PMID: 20370677.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20370677/
Cardillo C, Nambi SS, Kilcoyne CM, Choucair WK, Katz A, Quon MJ, Panza JA. Insulin stimulates both endothelin and nitric oxide activity in the human forearm. Circulation. 1999 Aug 24;100(8):820-5. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.100.8.820. PMID: 10458717.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10458717/
Ke JF, Wang JW, Zhang ZH, Chen MY, Lu JX, Li LX. Insulin Therapy Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Carotid Plaque in Type 2 Diabetes: A Real-World Study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Feb 1;8:599545. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.599545. PMID: 33598483; PMCID: PMC7882504.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33598483/
Brosolo G, Da Porto A, Bulfone L, Vacca A, Bertin N, Scandolin L, Catena C, Sechi LA. Insulin Resistance and High Blood Pressure: Mechanistic Insight on the Role of the Kidney. Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 23;10(10):2374. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102374. PMID: 36289636; PMCID: PMC9598512.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36289636/
Kumar M, Dev S, Khalid MU, Siddenthi SM, Noman M, John C, Akubuiro C, Haider A, Rani R, Kashif M, Varrassi G, Khatri M, Kumar S, Mohamad T. The Bidirectional Link Between Diabetes and Kidney Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Cureus. 2023 Sep 20;15(9):e45615. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45615. PMID: 37868469; PMCID: PMC10588295.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10588295/
Banks WA, Owen JB, Erickson MA. Insulin in the brain: there and back again. Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Oct;136(1):82-93. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.07.006. Epub 2012 Jul 17. PMID: 22820012; PMCID: PMC4134675.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22820012/
Rahman MS, Hossain KS, Das S, Kundu S, Adegoke EO, Rahman MA, Hannan MA, Uddin MJ, Pang MG. Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6403. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126403. PMID: 34203830; PMCID: PMC8232639.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8232639/
Scherrer U, Sartori C. Insulin as a vascular and sympathoexcitatory hormone: implications for blood pressure regulation, insulin sensitivity, and cardiovascular morbidity. Circulation. 1997 Dec 2;96(11):4104-13. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.11.4104. PMID: 9403636.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9403636/
Affuso F, Micillo F, Fazio S. Insulin Resistance, a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathological Mechanisms and a New Proposal for a Preventive Therapeutic Approach. Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 19;12(8):1888. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081888. PMID: 39200352; PMCID: PMC11351221.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11351221/
Park MH, Kim DH, Lee EK, Kim ND, Im DS, Lee J, Yu BP, Chung HY. Age-related inflammation and insulin resistance: a review of their intricate interdependency. Arch Pharm Res. 2014 Dec;37(12):1507-14. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0474-6. Epub 2014 Sep 20. PMID: 25239110; PMCID: PMC4246128.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25239110/
Hardy OT, Czech MP, Corvera S. What causes the insulin resistance underlying obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2012 Apr;19(2):81-7. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283514e13. PMID: 22327367; PMCID: PMC4038351.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4038351/
THIS WEBSITE PROVIDES INFORMATION FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. CONSULT YOUR HEALTH CARE PROVIDER FOR MEDICAL ADVICE.
Eat clean, drink filtered water, love, laugh, exercise outdoors in a greenspace, get some morning sunlight, block the blue light before bed, engage in meaningful work, find a sense of purpose, spend time with those you love, AND sleep well tonight.
Doctor Bob